Project management is the process of planning and controlling the development of a system within a specified timeframe at a minimum cost with the right functionality. A project manager has the primary responsibility for managing the hundreds of tasks and roles that need to be carefully coordinated.
Four Key Steps in Managing Projects :
- Identifying project size
- Creating and managing the workplan
- Staffing the project
- Coordinating and controlling project activities
Identifying Project Size
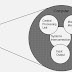
Project Manager’s Balancing Act - Project Management involves making trade-offs…
Modifying one element requires adjusting the others.
Project Estimation
- The process of assigning projected values for time and effort
- Sources of estimates (Methodology in use, Actual previous projects, Experienced developers)
- Estimates begin as a range and become more specific as the project progresses
Creating The Workplan
Identifying Tasks :
- Methodology (Using standard list of tasks)
- Top-down approach (Identify highest level tasks, Break them into increasingly smaller units, Organize into work breakdown structure)
List of all tasks in the work breakdown structure, plus :
- Duration of task
- Current task status
- Task dependencies
- Key milestone dates
Tracking Project Tasks :
- Gantt Chart (Bar chart format, Useful to monitor project status at any point in time)
- PERT Chart (Flowchart format, Illustrate task dependencies and critical path)
example :
- Tracking Tasks Using Gantt Chart
- Tracking Tasks Using PERT Chart
Staffing The Project
Staffing Attributes
- Staffing levels will change over a project’s lifetime
- Adding staff may add more overhead than additional labor
- Using teams of 8-10 reporting in a hierarchical structure can reduce complexity
Controlling Project Activities
CASE Tools :
CASE Components :
Standards Examples :
- Formal rules for naming files
- Forms indicating goals reached
- Programming guidelines
Documentation :
- Project binder
- Table of contents
- Continual updating
Managing Risk :
- Risk assessment
- Actions to reduce risk
- Revised assessment
Classic Mistakes :
- Overly optimistic schedule
- Failing to monitor schedule
- Failing to update schedule
- Adding people to a late project







0 comments:
Post a Comment